This sample shows how Row Level Security can be implemented in a Power BI (PBI) Embedded Application. The Power BI Service Subscription is owned by a Company ‘A’, and a PBI Pro User in this Organization builds the Reports and Datasets and publishes them to the Service. Since these reports would be accessed by Users in an external organization (Contoso, in this example), these reports are embedded in an ASP.NET Mvc Application.
About the data used in the Reports
The base data, shown in Figure 1, used in the Reports is from the table ‘Customers’ that contains a ‘Country’ Column. Sales Managers in Contoso are associated to one or more Countries. In this example a user johndoe@contoso.com is associated to 2 countries whereas others are associated to one each. It is required that when Sales Manager access the Reports, they ought to see only those Customers that lie in Country they are associated with.
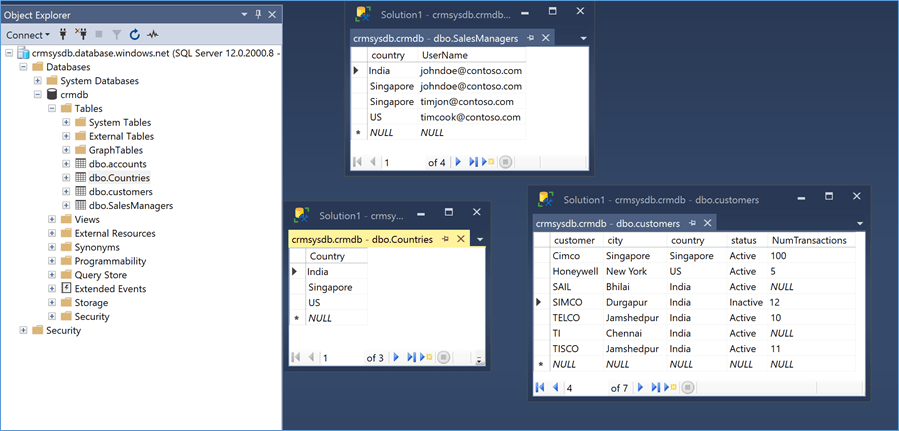
Figure 1 Azure SQL Database Tables
About the PBI Report and Data Set
A simple Tabular report layout, shown in Figure 2, is chosen to display the data. Relations were defined in the tables to relate the ‘Country’ Column in the ‘Customers’ and ‘SalesManagers’ Tables to the Master Table ‘Countries’ – Figure 3 below.
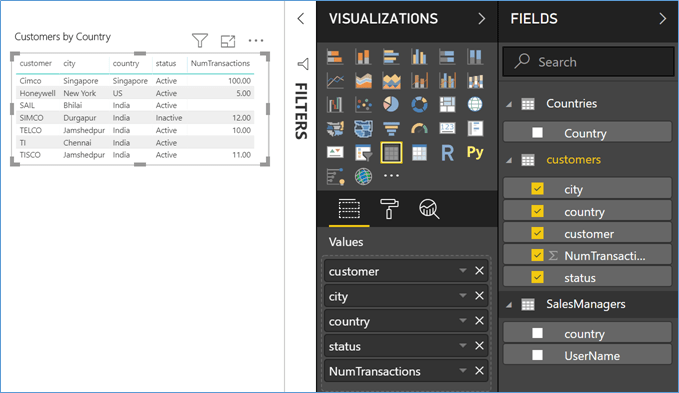
Figure 2 PBI Desktop Project
The security filter is set to bi-directional, as shown below.
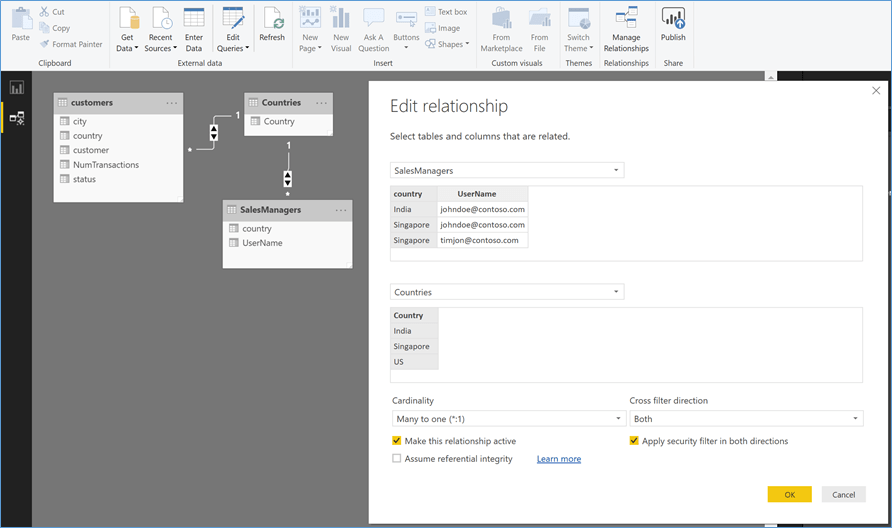
Figure 3 Customer Table Relations
Definition RLS in PBI Desktop
For RLS, we need a combination of Roles, Users and Rules
- Users
Users are defined in Azure SQL Database table (shown above).
| Note | Power BI Service provides the option where User to Role Mapping can be defined on the Report after it is published. Users can be picked up from Azure AD directly and assigned to the Roles. However, in this case, the users accessing the Report are external to the Organization hosting the reports and cannot be picked up from the Azure AD Tenant. These external Users are defined in the Database instead. |
- Roles & Rules
Roles ‘SalesManager’ and ‘SalesManagerIndia’ are defined in this sample. (See Figure 4 and Figure 5)
Rule for Role ‘SalesManager’ : Defined On Table ‘SalesManagers’, a DAX Expression is defined to return the Country Names associated to the User Name in the Request. In this case, if a SalesManager is linked to one or more countries, all those records will be returned.
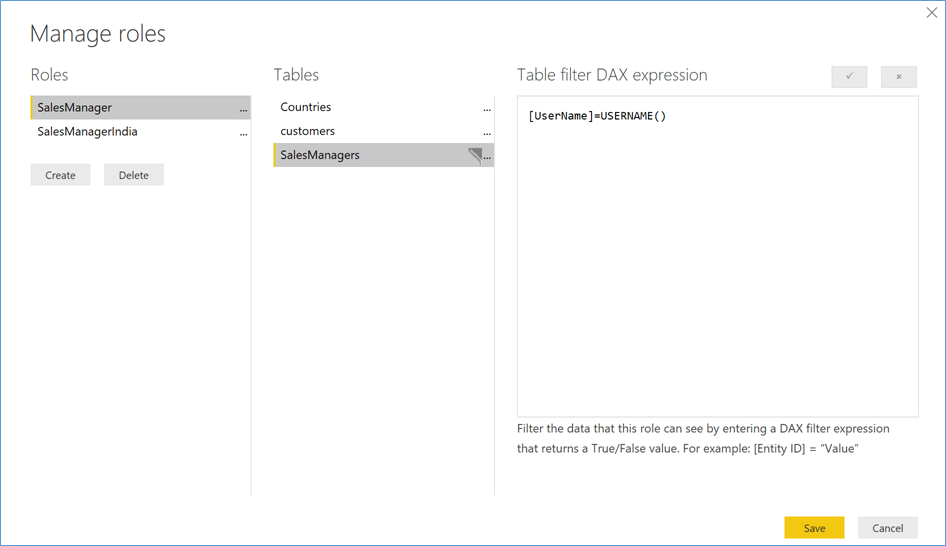
Figure 4 RLS Roles and Rules
Rule for Role ‘SalesManagerIndia’ : A UserName filter is applied on Table ‘SalesManagers’ as above, and additionally, an filter on ‘customers’ table is applied to filter only the records where the ‘Country’ is ‘India’. (See Figure 5)
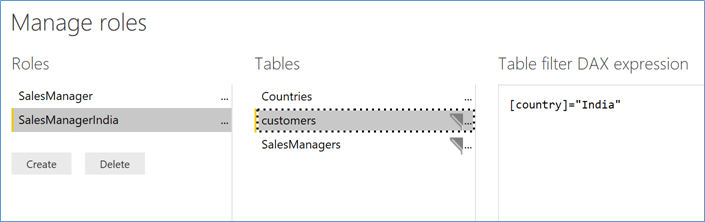
Figure 5 Roles & Rules
Testing the RLS in PBI Desktop
Selecting ‘SalesManager’ as Role and User ‘johndoe@contoso.com’ returns Customer records from both countries where this User is a SalesManager.

Figure 6 RLS -1
Selecting Role ‘SalesManagerIndia’ for the same User now returns only ‘Customers’ records in ‘India’. This shows that for the same User based on the Role Name, different RLS criteria can be applied.
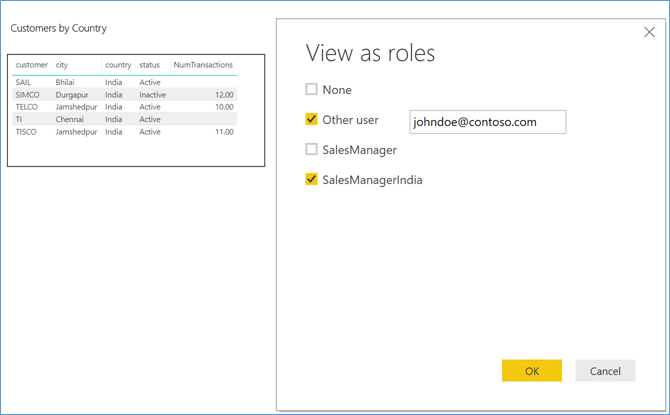
Figure 7 RLS – 2
Publish the Report
Publish the Report to Power BI Service. Next, embed the Report in an application. For this example, to embed this Report in an Application, the documentation steps and the sample ASP.NET Mvc Application provided in this link were used.
Running the PBI Embedded Application
Download the Visual Studio 2017 Solution for the sample Application referred above, make changes to the Web.config file to change the Report ID, Workspace ID in it to point to the ones used to deploy the Report in the earlier steps.
Launch the Solution locally from Visual Studio 2017, enter the User Name and Role name to check RLS.
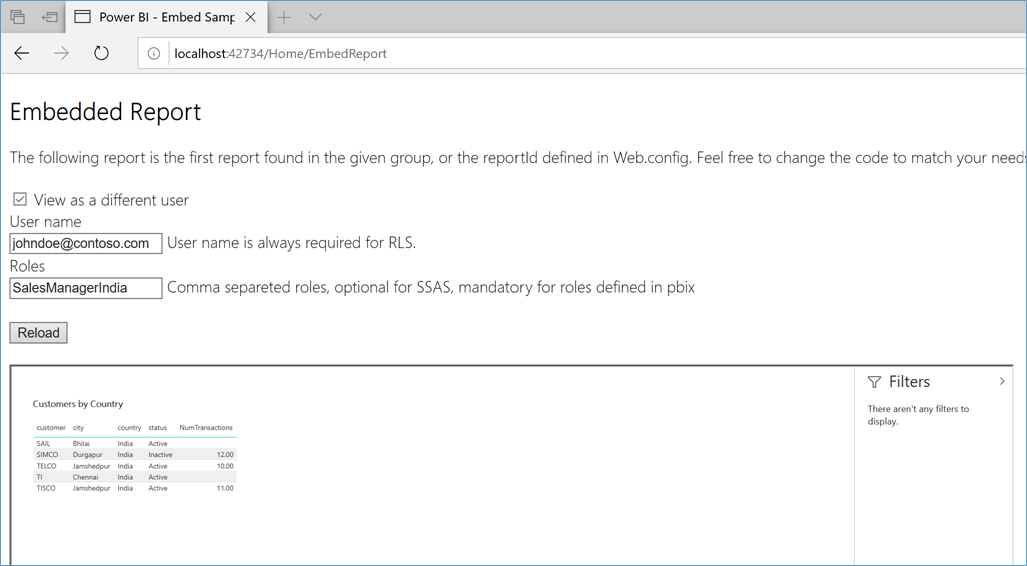
Figure 8 RLS on PBI Embedded Application